19.65.060 Landscaping types.
Below are the planting and design requirements for specific landscaping types. These landscaping types apply when required by different sections of code within this chapter and elsewhere in this division.
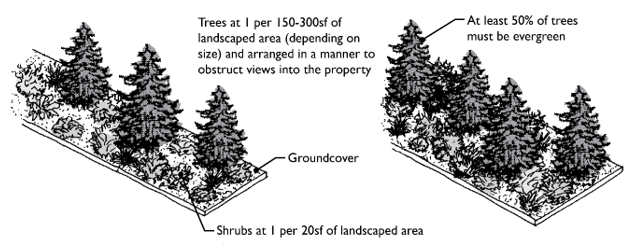
A. Type A Landscaping.
1. Purpose. Type A landscaping functions as a full screen and visual barrier. This landscaping is typically found between residential and nonresidential areas for screening unwanted views.
2. Screening Requirement. The selected plant materials and configuration must be able to screen 70 percent of the unwanted views within five years of planting and screen 100 percent of the unwanted views within six years of planting. This requirement must account for the size and characteristics of materials planted, their typical growth rate, and size at maturity.
3. Planting Requirements. Type A landscaping must minimally consist of the following:
a. Trees which are predominately evergreen (more than 50 percent).
b. Tree Size. A variety of tree sizes may be used, provided at least 70 percent are medium or large (see AMC 19.65.050(B)(1)). Trees must be planted at the following spacing standards (“on center” refers to the distance from other trees of any size):
i. Large trees must be spaced between 20 and 25 feet on center.
ii. Medium trees must be spaced between 15 and 20 feet on center.
iii. Small trees must be spaced between 10 and 15 feet on center.
c. Shrubs. Predominately evergreen provided at the rate of one shrub per 20 square feet of landscape strip.
d. Groundcover. Planted at a density to cover the buffer within three years.
e. Species Diversity. Trees and shrubs must comply with AMC 19.65.050(E).
DEPARTURES that vary from the planting requirements of this subsection (A)(3) will be considered, provided the proposal meets the screening requirement of subsection (A)(2) of this section.
|
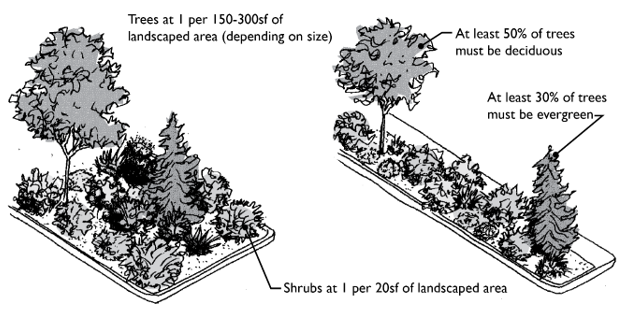
B. Type B Landscaping.
1. Purpose. Type B landscaping is a “filtered screen” that functions as a visual separator. This landscaping is typically found between differing types of residential development and used for screening unwanted views from the pedestrian environment.
2. Screening Requirement. The selected plant materials and configuration must meet the purpose of the standards within five years of planting. This requirement must account for the size and characteristics of materials planted, their typical growth rate, and size at maturity.
3. Planting Requirements. Type B landscaping must minimally consist of:
a. Trees which are at least 50 percent deciduous and at least 30 percent evergreen.
b. Tree Size. A variety of tree sizes may be used, provided at least 70 percent are medium or large (see AMC 19.65.050(B)(1)). Trees must be planted at the following spacing standards (“on center” refers to the distance from other trees of any size):
i. Large trees must be spaced between 20 and 25 feet on center.
ii. Medium trees must be spaced between 15 and 20 feet on center.
iii. Small trees must be spaced between 10 and 15 feet on center.
c. Shrubs. Provided at the rate of one shrub per 20 square feet of landscape strip and spaced no more than eight feet on center.
d. Groundcover. Planted at a density to cover the buffer within three years.
e. Species diversity: Trees and shrubs must comply with AMC 19.65.050(E).
DEPARTURES that vary from the planting requirements of this subsection (B)(3) will be considered, provided the proposal meets the screening requirement of subsection (B)(2) of this section.
|
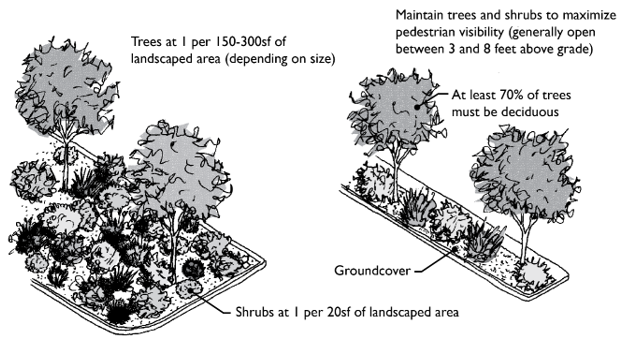
C. Type C Landscaping.
1. Purpose. Type C landscaping is a “see-through screen” that functions as a partial visual separator to soften the appearance of parking areas and building elevations. This landscaping is typically found along lot frontages or between multifamily developments.
2. Screening Requirement. The selected plant materials and configuration must meet the purpose of the standards within five years of planting. This requirement must account for the size and characteristics of materials planted, their typical growth rate, and size at maturity.
3. Planting Requirements. Type C landscaping must minimally consist of:
a. Trees which are at least 70 percent deciduous.
b. Tree Size. A variety of tree sizes may be used, provided at least 70 percent are medium or large (see AMC 19.65.050(B)(1)). Trees must be planted at the following spacing standards (“on center” refers to the distance from other trees of any size):
i. Large trees must be spaced between 20 and 25 feet on center.
ii. Medium trees must be spaced between 15 and 20 feet on center.
iii. Small trees must be spaced between 10 and 15 feet on center.
c. Shrubs. Provided at the rate of one shrub per 20 square feet of landscape strip and spaced no more than eight feet on center.
d. Groundcover. Planted at a density to cover the buffer within three years.
e. Species Diversity. Trees and shrubs must comply with AMC 19.65.050(E).
f. Maintain trees and shrubs to maximize pedestrian visibility (generally between three and eight feet above grade).
DEPARTURES that vary from the planting requirements of this subsection (C)(3) will be considered, provided the proposal meets the screening requirement of subsection (C)(2) of this section.
|
D. Type D Landscaping.
1. Type D landscaping refers to all other landscaped areas that do not qualify as Type A, B, or C landscaping, a hedge, or a rain garden. While native and low-maintenance trees and shrubs are encouraged in these areas, lawn areas may be used for recreational or design purposes. These areas may also include flower beds and perennial beds.
2. Type D landscaping may include any combination of plant materials, provided they comply with the plant materials standards in AMC 19.65.050.
E. Type E Landscaping—Low Hedge. A low hedge is intended to function as an attractive visual divider of space rather than a visual buffer between uses and properties. To qualify as a hedge landscaping type, the planting must be at least 30 inches wide and 30 inches tall. The hedge includes plant materials that typically grow no taller than five feet at maturity or are maintained between 30 inches and 48 inches tall.

|
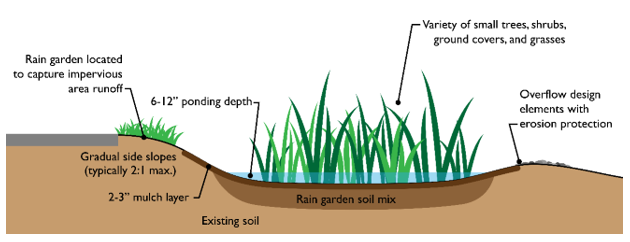
F. Type F Landscaping—Rain Garden.
1. A rain garden is a nonengineered planted depression that collects, absorbs, and filters rain water runoff from impervious areas. They are sized to accommodate temporary ponding and are not meant to be permanent ponds. They can also function as an attractive visual divider of space. To qualify as a rain garden, the following elements must be included:
a. Garden is located and designed to capture impervious area runoff.
b. Six- to 12-inch ponding depth.
c. Two- to three-inch mulch layer.
d. Gradual side slopes (typically 2:1 maximum).
e. Overflow design elements with measures to prevent erosion.
f. Generous plantings of a variety of small trees, shrubs, groundcovers, and grasses. Select plants suitable for the planting zones within the garden and around the perimeter.
Refer to the current Rain Garden Handbook for Western Washington for further guidance on rain garden location, design, planting, construction, and maintenance. Compliance with the Stormwater Management Manual may alter these requirements.
2. The applicability of rain gardens in site design will be determined by project size and flow control exemptions based upon minimum requirement No. 5 of the Western Washington Phase II municipal stormwater permit.
|
(Ord. 4022 § 1 (Att. A), 2022; Ord. 3040 § 2 (Att. A), 2019)